
Have you ever seen a cement truck on a construction site and wondered how those trucks work? Why does the barrel rotate? Will the cement inside dry and if so, how does that affect your cement load? If these facts capture your interest, then this article is for you.
Below we’ll take a look at the history of cement trucks and how they work. We’ll also answer a few of the more commonly asked questions about these mixer trucks. Read on as we dive right into the ins and outs of cement mixers.
What Is a Cement Truck?
A cement truck, often referred to as a cement mixer, is a heavy-duty vehicle used in the construction industry. They carry ready-mixed concrete to building or construction sites. The mixer truck features a mixing drum and specialised mixing mechanisms. Concrete is mixed inside the rotating drum.
History of Cement Trucks
The first concrete mixer was developed in 1900 by T.L. Smith in Milwaukee. The basic construction of the drum started out as a double cone with blades. The original patent for this type of truck labelled the vehicle as an “Apparatus for Concrete Work.” Over the years, this design has remained very similar but now features a tiltable conical drum.
It wasn’t until after World War II that cement trucks gained popularity. This was largely because of an increased demand for concrete to rebuild buildings that were damaged during the war.
Basic Setup of a Cement Truck
Essentially, cement mixers are equipped with two or more axles. The most common types are four, five and six-axle trucks. The number of axles used is determined by the load required as well as local legislation for heavy machinery on specific roads.
Axles distribute the load evenly and reduce the normal wear and tear on regular roads. Specialised concrete mixers such as those found at Syntech boast mixer drums with a capacity ranging from 8m3 – 12m3. Additionally, some cement trucks also feature Hardox technology that is perfect for low-weight, wear resistance and higher load capacities.

How Does a Cement Truck Work?
Concrete trucks, or in-transit mixers, are designed to mix and transport concrete to building sites.
Essentially these types of mixers are loaded with dry materials and water and set to mix during transport. Alternatively, the cement mixer can also be loaded with a “central mix” where the required cement has been pre-mixed prior to loading. The cement mixer then keeps the cement in a liquid state through agitation (turning of the drum) until delivery.
Step-By-Step Guide for How a Cement Truck Works
For a clearer understanding of how a cement truck works, we’ve broken it down into an easy-to-follow step-by-step guide.
- Concrete mixer trucks have an interior turbine that pushes the mixed concrete against the gravity of the drum.
- Dry concrete mix, made up of cement, sand and aggregates are added to the drum and water can be added before transport. Some cement mixers feature a water tank, which allows the driver to mix the cement closer to the job site. This is especially handy in instances where the cement company is far from the job site.
- A spiral blade works in a rotational direction and pushes the concrete deeper into the drum to mix and prevent it from drying during transport.
- The direction the drum rotates in while transporting is referred to as “charging” the mixer. This refers to the continuous “stirring” of the cement to keep it in its liquid state.
- When it’s time to release the cement, an Archimedes’ screw-type application “discharges” the cement out of the drum.
- Depending on the design of the truck, the cement may flow onto chutes to guide the sticky concrete onto the area it needs to be (sidewalks for instance).
- If a cement mixer can’t reach the area where the cement must be dropped, construction workers opt to use a concrete pump. The concrete pump is ideal for getting concrete to multi-floor buildings or other high structures where the building is taking place.
- Building sites need to be prepared in advance to avoid any delays once the truck arrives as leaving the cement for too long will cause it to harden, rendering it useless.
- In some cases, drivers will wash out the cement truck drum at the job site to prevent any residual cement from hardening.
We’ve added a short clip below to show you how these steps work!
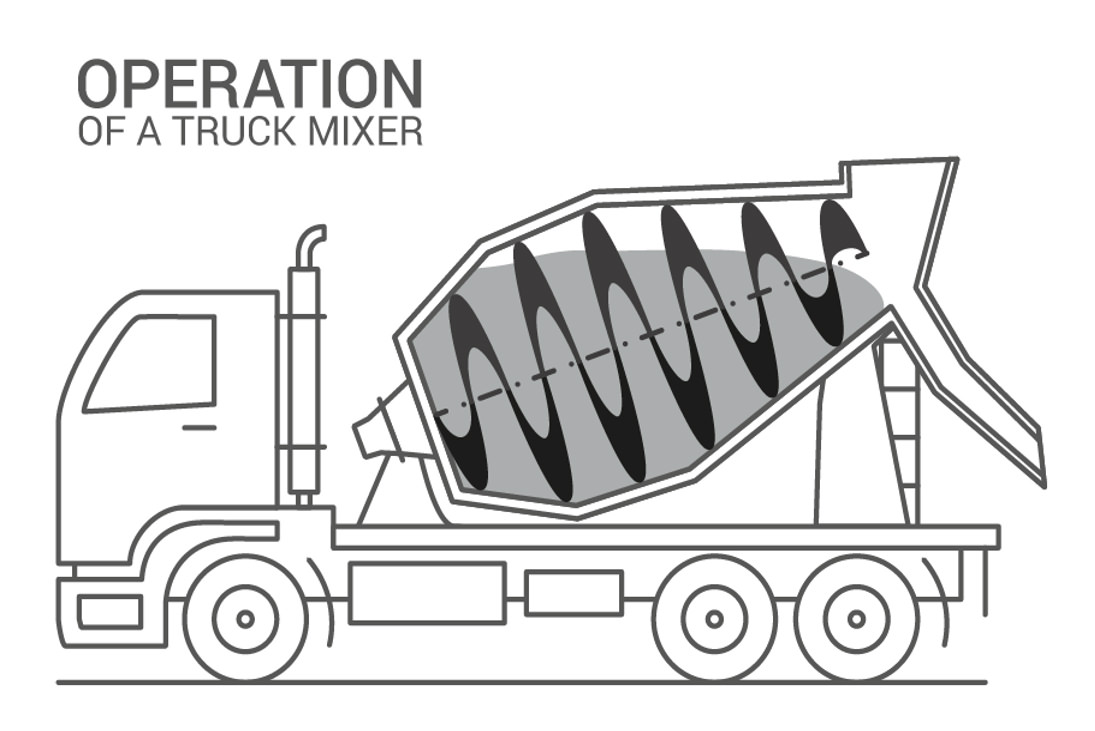
Image from Wikipedia – Operating diagram illustrates how the cement is mixed
How Long Can You Keep Cement in a Cement Truck?
Most cement manufacturers advise that concrete should be discharged from the mixer within two hours of starting the mixing process. Otherwise, the cement will start hardening.
For this reason, construction managers only request cement mixer trucks to be dispatched once the construction site has been prepared. That way the truck starts discharging as soon as it arrives on site.
How Much Cement is Usually in a Cement Truck?
Generally, most concrete trucks can hold between 11 and 15 cubic yards of concrete. Weight limits on roads in some countries might limit the allowed amount to between 8 and 11 cubic yards.
What are Cement Trucks Used For?
Essentially, cement mixer trucks are used on building sites where it isn’t always possible or practical to mix concrete on site. Since the concrete is delivered finished, on-demand and in the specific quantity needed, it’s ideal for the following uses:
- Creating sidewalks and road structures
- Laying asphalt for roads
- Various applications on new structures such as multi-floor buildings
FAQs
1. How does cement not dry in the truck?
Simply put, many mobile cement mixers contain a separate water tank inside the back of the truck. This enables the driver to mix water with the dry ingredients-aggregate and cement-whenever necessary. For maximum results, the driver will release the water to mix the cement when just a few kilometres from the job site. Doing this ensures that the cement is mixed properly and ready for use.
2. How do they clean the inside of cement trucks?
As the cement dries, the leftover concrete builds up in the cement mixer. Additionally, a thin film of cement will remain in the drum even when it’s been emptied. Washing this cement out is best achieved by using an abrasive type of aggregate to scrub the inside of the drum. Using a mixture of cleaning stabilisers is also an effective washing method.
3. Are cement trucks automatic or manual?
For the most part, concrete trucks come with either automatic or manual transmissions. Most older trucks featured manual transmissions, but newer models tend to be automatic. An automatic version allows the driver to utilize the truck more effectively.
4. Why do cement trucks rotate?
Generally, the type of concrete mixer used will depend on the type and amount of concrete needed at the job site. Ready-mix concrete trucks can work as a cement agitator or mixer. Having a rotating barrel keeps the concrete at the right texture by continuously mixing the wet and dry elements in the drum/barrel.
5. What happens if cement dries in a truck?
When cement inside the drum/barrel starts drying, the build-up slows down the mixer’s capacity. This happens because the dried cement fills the inner section of the drum. As a result, you won’t be able to fill the drum as full as usual.
Consequently, this dry cement also makes the truck heavier which in turn requires more fuel and isn’t very cost-effective. It’s always an economical idea to prevent cement drying in the truck and perform regular washouts.
Conclusion
It’s clear that cement mixers aren’t as complex as you might have thought. Once you understand the basic principles, it’s easy to see why these versatile trucks are necessary around almost every construction site.
If you’re looking for a company to fit or design your cement truck, be sure to contact Syntech. Despite being based in Singapore, they’re also available in Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines and Vietnam. Mixing the cement on the way to the job site saves time and money. It’s the perfect way to keep your building project on schedule.
